Using the CSS Language There are 6 Common Ways to Specify Colors:
Named Colors: CSS includes a predefined set of named colors, like
red,blue,yellow, etc. There are approximately 140 standard color names.Here are the colors sorted by their names: https://www.w3schools.com/colors/colors_names.asp
The popular CSS library Tailwind also includes its own set of named colors listed here: https://v2.tailwindcss.com/docs/customizing-colors
Hexadecimal (Hex) Notation: Colors can be defined using a
#followed by a 6-digit hexadecimal value. For example:#FF0000is red. Shortened 3-digit hex codes can also be used, such as#F00for red or#FFFfor white.RGB: Stands for Red, Green, and Blue. Colors can be defined using the
rgb()function, for instance:rgb(255,0,0)is red andrgb(255,255,255)is whiteRGB notation is decimal notation as compared to Hexadecimal notation
255 decimal is equivalent to FF Hexadecimal
RGBA: The 'A' stands for Alpha (opacity). The rgba() function lets you specify colors with opacity. For instance:
rgba(255,0,0,0.5)is semi-transparent red.HSL: Stands for Hue, Saturation, and Lightness. An example is
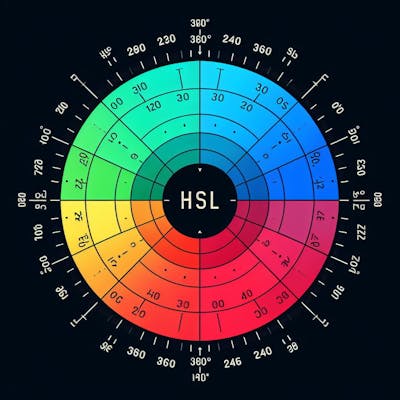
hsl(0, 100%, 50%)which represents red.- The HSL color model, which stands for Hue, Saturation, and Lightness, provides a more intuitive way to represent and manipulate colors compared to the RGB model. In HSL, 'Hue' determines the type of color and is represented as an angle from 0° to 360°, where common values like 0° signify red, 120° for green, and 240° for blue. 'Saturation' defines the intensity or purity of that hue, with values ranging from 0% (a shade of gray) to 100% (the fullest color). Lastly, 'Lightness' describes the brightness of the color, where 0% is black, 100% is white, and 50% exhibits the most authentic hue. Together, these three components allow for an intuitive understanding of color.
HSLA: Similar to HSL but with an Alpha (opacity) channel, for example:
hsla(0, 100%, 50%, 0.5)
The Color Wheel

The concept of the color wheel dates back to Sir Isaac Newton's experiments in 1666. Using a prism, he discovered that white light disperses into various colors of the visible spectrum. To illustrate this, he arranged these colors in a circular manner, laying the foundation for the modern color wheel. Over the centuries, artists have adapted this concept to better understand color mixing, defining primary colors, from which all other shades could be derived, and secondary colors, the result of blending two primaries. For example, mixing red and blue gives the color purple.
HSL Model of Understanding Color
Going back to the HSL model we can think of Hue as a circular color wheel:
Red sits at 0° (or 360°, as it's a circle).
Green is at 120°.
Blue is at 240°.
Saturation tells us how vibrant or muted the color is, with 0% being gray and 100% being the most vibrant.
Finally, Lightness adjusts the shade from black (0%) to the true hue (50%) to white (100%). So, by playing with HSL values, you can pinpoint any color you want on this wheel.
Given this information on HSL and remembering mixing red and blue make purple. We can intuitively guess that purple would be between 240 and 360 degrees on the Hue color wheel. However, the exact hue value can vary depending on the specific shade of purple you're referring to, as "purple" can encompass a range from a more bluish-violet to a reddish-magenta.
Visual Color Picker
W3schools website has a nice chart for easily picking out colors as well as translating colors between the various syntaxes. Take a look at it and play around.
https://www.w3schools.com/colors/colors_picker.asp?colorhex=34568B
Top 7 usages of the keyword color in CSS
The keyword color in CSS is primarily used to define text color, but its influence doesn't stop there. Here are the top 7 usages of the keyword color in CSS:
Text Color:
The
colorproperty is used to define the color of text. For instance:p { color: blue; }
This would set the color of the text inside all <p> elements to blue.
Background Color:
The
background-colorproperty is used to define the color of the background. For instance:p { background-color: green; }
This would set the background color of the text inside all <p> elements to green.
Border Color:
The
border-colorproperty is used to define the color of a border. For instance:p { border-color: green; }
This would set the background color of the text inside all <p> elements to green.
currentColor:
currentColoris a special keyword in CSS that represents the computed value of thecolorproperty for a given element. This can be used with other properties to maintain consistency. For example:button { color: red; border: 2px solid currentColor; }
Here, the border of the button will be the same color as the text (red).
SVG Styling:
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) often uses the
colorproperty to influence certain parts of its styling. For example, thefillandstrokeproperties in SVG can inherit the color set by thecolorproperty:svg { color: green; } path { fill: currentColor; }
This would set the fill color of the SVG path elements to green.
List Marker Color:
The
colorproperty can influence the color of list markers (bullets or numbers) in unordered and ordered lists.ul { color: purple; }
This would set the color of the list markers in an unordered list to purple.
Pseudo-elements:
The
colorproperty can also be applied to pseudo-elements like::beforeand::after, influencing the color of content generated by these pseudo-elements.div::before { content: "★"; color: gold; }
This would prepend a gold star symbol to the content of a <div>.
While the primary usage of the color property is for text styling, its influence extends to various other areas, making it an integral part of CSS.
CSS Variables and Colors
With the advent of CSS custom properties, it's now possible to define color variables for reuse throughout your stylesheets. For example: --main-bg-color: #FF5733; and then use var(--main-bg-color) to apply it.
Color Functions, SASS and LESS
CSS has introduced color-modifying functions like lighten(), darken(), and saturate() but currently, these are mostly used with CSS preprocessors like SASS or LESS. However, in the future expect to see more direct color manipulation within CSS itself with CSS Color Module Level 4. Info here --> https://www.w3.org/TR/css-color-4/

Dark Mode, CSS color and more
Adapting your website's colors for dark mode involves responding to a user's system preference with the prefers-color-scheme media query in CSS. Here's a brief explanation:
Detecting Dark Mode: Use the
prefers-color-schememedia query to detect if a user has chosen a dark or light interface theme in their system settings./* Light mode styles (default) */ body { background-color: white; color: black; } /* Dark mode styles */ @media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) { body { background-color: black; color: white; } }CSS Variables for Flexibility: To make switching between color schemes smoother and more manageable, consider using CSS custom properties (variables).
/* Define default (light mode) colors */ :root { --background-color: white; --text-color: black; } /* Override for dark mode */ @media (prefers-color-scheme: dark) { :root { --background-color: black; --text-color: white; } } body { background-color: var(--background-color); color: var(--text-color); }Additional Considerations for dark mode:
When designing for dark mode, it's not just about inverting colors. It's essential to ensure that colors maintain proper contrast for readability.
Consider other elements like images, borders, and shadows. They might also need adjustments for dark mode to ensure a harmonious appearance.
Some websites provide a toggle button for users to switch between light and dark modes manually, overriding the system preference. Implementing this requires a bit of JavaScript along with CSS.
With these basics, you can start adapting your website to be more user-friendly in both light and dark environments.
The Tailwind CSS Frameworks & Dark Mode:
Modern CSS frameworks, such as the popular Tailwind CSS, have significantly simplified the process of implementing dark mode. Tailwind, for instance, provides utility classes that can be easily toggled based on user preferences without writing custom media queries. By configuring your Tailwind setup and adding a simple dark variant, you can prepend your utility classes with dark: to style elements specifically for dark mode. This streamlined approach not only reduces the amount of custom CSS required but also ensures a more consistent and maintainable codebase.